Glucagon Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1): An Increasing Trend in Potential Misuse
The purpose of this article is to create awareness of potential misuse of GLP-1 RAs for non-FDA approved indications.

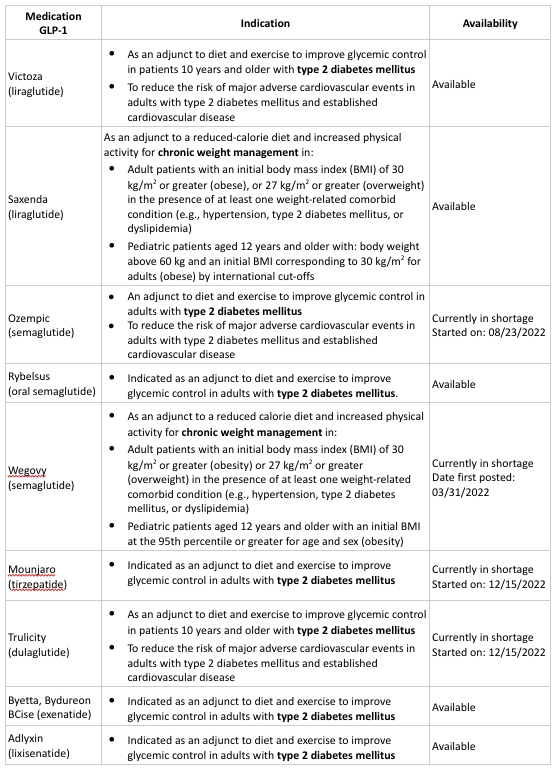
For the last couple of years, glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) have been used to effectively treat type 2 Diabetes Mellitus due to their ability to aid in arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) by providing diabetes improvement and weight loss with low risk of hypoglycemia. Recently, the New England Journal of Medicine published articles on the use of GLP1-RAs: tirzepatide and semaglutide as effective medications for the management of obesity. It is important to note that currently only two GLP-1 RA agents have the indication for management of obesity: Wegovy (semaglutide) and Saxenda (liraglutide).
In 2021, Wegovy (semaglutide), a product with the same active ingredient as Ozempic (semaglutide) was released for the treatment of obesity showing a reduction of 15% body weight in clinical trials. The clinical evidence resulted in a rising trend in GLP-1 RAs utilization with a potential for misuse. Our goal is to review some of the factors that led to the GLP-1 RAs increase in utilization and offer recommendations to providers and payers.
As research advances, GLP-1 RAs represent another treatment option for patients that struggle with obesity along with other comorbidities such as: hypertension and dyslipidemia. Upon the release of information regarding the benefits of GLP-1 RAs in weight loss, news spread on social media about the medication that labels it as a simple way to lose weight. However, in order to receive Wegovy, patients should meet specific criteria for weight loss. According to the drug package insert, to qualify for Wegovy treatment, adult patients must have 30 kg/m2 or greater (obesity) or 27 kg/m2 or greater (overweight) in the presence of at least one weight-related comorbid condition (e.g., hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or dyslipidemia). Wegovy is also indicated for pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with an initial BMI at the 95th percentile or greater for age and sex (obesity). There are concerns that patients receiving prescriptions for Wegovy do not meet these criteria, which is leading to overutilization and a shortage of these medications (Wegovy and Ozempic) as reported by the ASHP and other health organizations. It is important to note that Wegovy and Ozempic are not interchangeable, have different indications, and are used at different dosage strengths as established by the FDA. Due to this shortage, patients may not have access to Ozempic for the treatment of diabetes.
During the Ozempic shortage, there are treatment alternatives that may be recommended for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. It is important for patients to consult with their doctor regarding other GLP-1 RA options such as Victoza (liraglutide), Trulicity (dulaglutide), Byetta or Bydureon BCise (exenatide), Rybelsus (oral semaglutide), Mounjaro (tirzepatide), Adlyxin (lixisenatide), etc.
For persons diagnosed with obesity and unable to access Wegovy, there may be other treatment options or weight loss programs available. It is important to note that not all insurance benefits cover weight loss treatments. Beneficiaries diagnosed with obesity should confirm their insurance benefits first and consult with their doctor regarding treatment options. Other FDA approved medications for weight loss include: Saxenda (liraglutide), Contrave (naltrexone/bupropion), Qsymia (topiramate/phentermine), Xenical (orlistat; generic: Alli). In addition, establishing a healthy diet and exercise recommended by health professionals may aid in weight loss and general health.
References:
- American Diabetes Association. (2023). Standards of Care in Diabetes (Vol. 46, Ser. Suppl 1).
- Drug shortage detail: Semaglutide injection. ASHP (2023). from https://www.ashp.org/drug-shortages/current-shortages/drug-shortage-detail.aspx?id=813&loginreturnUrl=SSOCheckOnly
- Dungan, K., & Desantis, A. (2022). Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Retrieved from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/glucagon-like-peptide-1-based-therapies-for-the-treatment-of-type-2-diabetes-mellitus?search=GLP1%20shortage&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1#references.
- FDA Approved Drugs. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2023) from https://www.access.fda.gov/
- FDA Drug Shortages. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2023) from https://www.access.fda.gov/
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2017). OZEMPIC (semaglutide) injection, for subcutaneous use.
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2021). WEGOVY (semaglutide) injection, for subcutaneous use.
- Jastreboff, A., Alves, B., Connery, L., Wharton, S., Ahmad, N., Aronne, L., Stefanski, A., Bunck, M., Liu, B., Zhang, S., & Kiyosue, A. (2022). Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity. New England Journal of Medicine, 387(15), 1433–1435. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmc2211120
- Landwehr, J. (2022). Ozempic shortage: How a viral trend could be putting people with diabetes at risk. Health. Retrieved from https://www.health.com/ozempic-wegovy-shortage-weight-loss-diabetes-risk-6823914
- Wilding, J., Batterham , R., Calanna, S., Davies, M., Van Gaal, L., Lingvay, I., McGowan, B., Rosenstock, J., Wadden, T., Wharton, S., & Yokote, K. (2021). Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. New England Journal of Medicine, 385(1). https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmc2106918